No Energy Security for Japan Without Optimizing Nuclear Source
As Japan grapples with the ongoing challenges of energy dependency and security, the spotlight increasingly falls on its nuclear energy sector. Following the Fukushima disaster in 2011, public sentiment and regulatory scrutiny surrounding nuclear power have created hurdles that hinder its full revival. Yet, with global energy markets becoming more volatile and the urgent need for carbon neutrality intensifying, Japan is at a crossroads. A extensive strategy to optimize its nuclear energy capabilities is not just beneficial—it is vital. This article delves into the current state of Japan’s nuclear energy landscape, the implications for national energy security, and the necessity of a balanced dialog that integrates safety, innovation, and sustainability in nuclear technology. As Japan seeks a stable energy future, understanding the crucial role of nuclear power may well determine the country’s resilience in an unpredictable energy surroundings.
Nuclear Energy as a Cornerstone for Japans Energy Security
As Japan grapples with its energy challenges, leveraging nuclear power emerges as a crucial strategy for ensuring stable energy supply and reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels. Following the 2011 Fukushima disaster, public sentiment towards nuclear energy saw a significant downturn, yet advancements in technology and enhanced safety protocols have transformed the landscape. Today, modern reactors are designed with robust safety features that dramatically lower risks, reinstating confidence in nuclear energy as a reliable source. The key advantages of revitalizing nuclear energy include:
Energy Independence: Reducing reliance on foreign energy sources contributes to national sovereignty.
Low Carbon Emissions: Nuclear power produces minimal greenhouse gases, aligning with Japan’s commitment to environmental sustainability.
High Energy Yield: A single nuclear reactor can generate a significant amount of energy, making it efficient compared to other sources.
To effectively implement a nuclear strategy,Japan must explore various avenues for optimizing its nuclear capabilities. This includes investing in research and advancement for advanced reactors,enhancing decommissioning processes for older plants,and implementing comprehensive public outreach programs to rebuild trust in nuclear technology. By addressing these areas,Japan can create a more resilient energy framework. A strategic approach may involve:
Focus Area
Proposed Action
Safety Enhancements
Adopting next-generation safety standards and technologies
Community Engagement
Implementing educational programs to inform the public
Resource Management
Investing in lasting waste management solutions
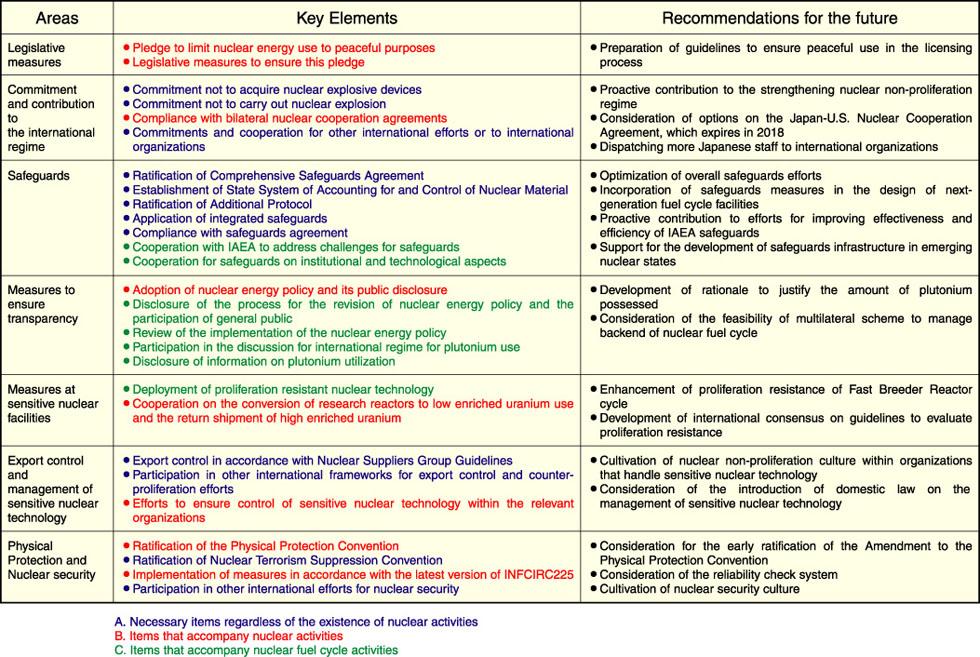
Challenges and Opportunities in Japans Nuclear Regulatory Framework
Japan’s nuclear regulatory framework faces significant challenges that stem from its complex history and the aftermath of the Fukushima disaster. Key issues include:
Public Trust: A significant portion of the Japanese population remains wary of nuclear energy due to safety concerns, which affect regulatory decisions and public policy.
Safety Standards: stricter safety standards imposed by the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) enhance security but can lead to delays in reactor restarts.
Technological Innovation: Balancing the need for advanced technology with stringent regulatory compliance presents hurdles for operators aiming to enhance safety and efficiency.
However, these obstacles also pave the way for new opportunities within the nuclear sector. By embracing modernization and openness, Japan can revitalize its regulatory approach. Potential avenues include:
International Collaboration: Partnering with leading global nuclear safety organizations to adopt best practices and innovative technologies.
Public Engagement: Initiating dialogue with communities to rebuild trust and foster understanding about the safety measures in place.
Investment in Research: Allocating resources to research and development can lead to innovative solutions that address safety and environmental concerns.

Strategies for Enhancing Public trust in Nuclear Energy Initiatives
To bolster public confidence in nuclear energy initiatives, it is indeed crucial for stakeholders to foster transparency and open interaction. Engagement with local communities can significantly enhance understanding and acceptance of nuclear projects. Key strategies include:
regular Public Consultations: Hosting forums and workshops to educate residents about nuclear technology, safety measures, and environmental impacts.
Transparent reporting: Sharing data and findings related to safety protocols and the environmental footprint of nuclear facilities can demystify operations.
Collaborative Partnerships: Building alliances with local organizations,schools,and environmental groups to promote mutual understanding and trust.
In conjunction with communication, investment in innovative technologies and rigorous safety measures is imperative. Demonstrating a commitment to high standards can reassure the public regarding the safety of nuclear energy. Strategies that can be employed include:
Advanced Safety Features: Implementing state-of-the-art safety systems that exceed regulatory requirements.
Autonomous Oversight: Encouraging third-party evaluations of safety and environmental practices to ensure accountability.
Emergency Preparedness Plans: Developing and sharing comprehensive emergency response strategies with the community.

Innovative Technologies and Their Role in modernizing Japans Nuclear Infrastructure
Japan’s nuclear infrastructure stands at a critical juncture, necessitating the adoption of innovative technologies to enhance safety, efficiency, and reliability. The implementation of smart grid systems and advanced nuclear reactors forms the backbone of modernization efforts. These technologies not only improve operational efficiency but also integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources, creating a resilient power network. Key advancements include:
Passive Safety Features: New reactor designs incorporate systems that automatically ensure safe cooling without human intervention.
Digital Monitoring Systems: Enhanced surveillance using AI and machine learning optimizes maintenance schedules and predicts potential failures.
Modular Reactors: smaller, scalable reactors provide flexibility for energy production tailored to local demands.
Moreover, the integration of Blockchain technology promises to revolutionize the management of energy transactions and regulatory compliance. With such innovations, Japan can achieve greater transparency and efficiency in its nuclear supply chain, thereby fostering public trust in the sector. To illustrate the potential impact of these technologies, consider the following comparison of traditional versus modern nuclear systems:
Aspect
Traditional Nuclear Systems
Modernized Nuclear Systems
Efficiency
Lower fuel utilization
Higher fuel efficiency with advanced reactors
Safety Measures
reliant on manual checks
Automated safety protocols
Integration
Standalone operations
Integrated with renewable sources
The Way Forward
Japan stands at a critical crossroads in its energy policy. As the nation grapples with the challenges of energy security in a rapidly evolving geopolitical landscape, the optimization of its nuclear energy sources emerges as a pivotal solution. With the pressing need to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and enhance energy independence, Japan must prioritize the safe and efficient integration of nuclear power into its energy mix. By addressing regulatory hurdles and investing in modern technologies, the country can harness the potential of nuclear energy to provide a stable, sustainable, and secure energy future.As Japan moves forward, the commitment to nuclear energy not only supports national security but also aligns with global initiatives for reducing carbon emissions. The path that Japan chooses now will shape its energy landscape for decades to come, influencing not only economic stability but also the prosperity and well-being of future generations.
Author : Charlotte Adams
Publish date : 2025-02-27 23:04:14
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.